The purpose of this example is to demonstrate on how the Message Bus EIP pattern is supported through the WSO2 ESB. The purpose of the Message Bus is to allow This section explains how the Message Bus EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Introduction to Message Bus
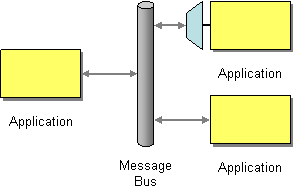
The Message Bus EIP enables separate applications to work together in a decoupled manner . Which in return will make the maintenance, testing smoother since editing or removal of so that applications can be easily added or removed without affecting each other. This approach makes maintenance and testing smoother, since editing or removing an application will not affect the functionality of any other application.
...
For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/MessageBus.html.
Figure 1: Message Bus EIP
How WSO2 ESB implements the EIP
The architecture of the WSO2 ESB is discussed clearly in Architecture in the WSO2 ESB Architecturedocumentation. Which It illustrates how each application logic is layered. Also notice that each , and how each component of the application logic has being is separated as a mediator where the , allowing message processing is done to be executed in a decoupled manner. The mediation process is best explained in Message Mediation. The below illustrates a sample ESB configuration. the Mediating Messages section of the WSO2 ESB documentation.
A sample ESB configuration is illustrated below:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<!-- filtering of messages with XPath and regex matches -->
<filter source="get-property('To')" regex=".*/StockQuote.*">
<send>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</endpoint>
</send>
<drop/>
</filter>
<send/>
</definitions> |
The above configuration will route According to the configuration above, the ESB routes an incoming message to a back-end server if the conditions mentioned in the filer filter section are met. Notice and see how each the application's logic has being is decoupled. For filtering its It uses one component for filtering, and another to send a message to the endpoint its another, where the fact is apparent that in case if the user desires the filtering is unnecessary all he or she should do is . If you were to decide to remove the filtering step, you could remove the filter mediator out of segment from the XML , which in return will not affect without affecting the application's logic of for sending the message to the back end.
...
| hidden | true |
|---|
...
-end server.