This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Recipient List EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Recipient List
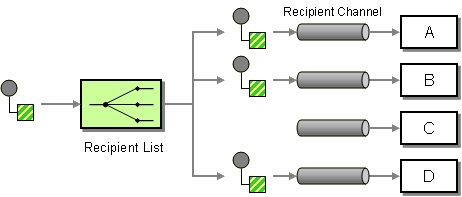
The Recipient List EIP routes a message to a list of dynamically specified recipients. It processes an incoming message and identifies its list of recipients. Once the list is identified, the message will be sent to all recipient channels. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/RecipientList.html.
Figure 1: Recipient List EIP
Example scenario
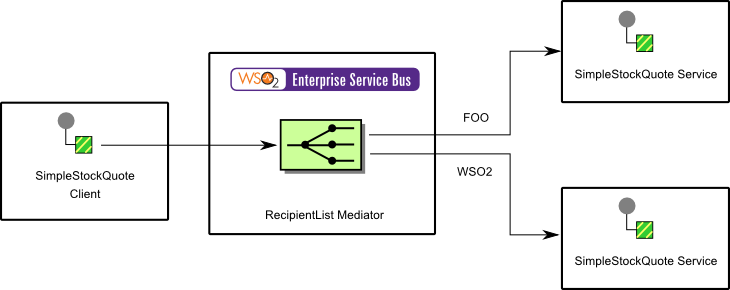
This example scenario is a stock quote service sending a stock quote request to recipients that are instances of a sample Axis2 server. The Switch mediator identifies the content of the client request and distributes the content among the Recipient List endpoints.
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using the WSO2 ESB.
Figure 2: Recipient List Example Scenario
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Recipient List EIP by comparing their core components.
| Recipient List EIP (Figure 1) | Recipient List Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Sender | StockQuoteClient |
| Recipient List | RecipientList mediator |
| Receivers (A, B, C, D) | SimpleStockQuote Service Instances (foo, WSO2) |
Environment setup
- Download and install WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, refer to Installation Guide in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Deploy the
SimpleStockQuoteServiceand start three instances of Axis2 Server in ports 9000, 9001, 9002, and 9003. For instructions, refer to the section Setting up the ESB Samples - Starting the Axis2 server in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ESB configuration
Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (https: //localhost:9443/carbon
). In the management console, navigate to the Main menu and click Source View in the Service Bus section. Next, copy and paste the following configuration, which helps you explore the example scenario, to the source view.
<!-- Would Route the Message Based on the List of Recipients-->
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<registry provider="org.wso2.carbon.mediation.registry.ESBRegistry">
<parameter name="root">file:repository/samples/resources/</parameter>
<parameter name="cachableDuration">15000</parameter>
</registry>
<proxy name="RecipientListProxy">
<target>
<inSequence>
<switch source="//m0:getQuote/m0:request/m0:symbol" xmlns:m0="http://services.samples">
<!-- First the recipient list will be identified -->
<case regex="foo">
<send>
<!--Dynamic Recipient List-->
<endpoint>
<recipientlist>
<endpoint xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</endpoint>
<endpoint xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<address uri="http://localhost:9001/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</endpoint>
</recipientlist>
</endpoint>
</send>
<drop/>
</case>
<case regex="WSO2">
<send>
<!--Dynamic Recipient List-->
<endpoint>
<recipientlist>
<endpoint xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<address uri="http://localhost:9002/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</endpoint>
<endpoint xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<address uri="http://localhost:9003/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</endpoint>
</recipientlist>
</endpoint>
</send>
<drop/>
</case>
<default>
<!-- Message Should Be Discarded -->
</default>
</switch>
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send/>
</outSequence>
</target>
</proxy>
</definitions>
Simulating the sample scenario
Send a request using the Stock Quote client to WSO2 ESB in the following manner. For information about the Stock Quote client, refer to the Sample Clients section in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ant stockquote -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:8280/services/RecipientListProxy -Dsymbol=WSO2
Note that the ESB sends the request to servers running on ports 9002 and 9003. If you change the symbol to foo, it will send the requests to servers running on port 9000 and 9001.
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below are mapped with the ESB configuration shown above.
- Switch [line 10 in ESB config] - The Switch mediator performs a switch/case based on the symbol found inside the original request. In this example scenario, one of two send mediators are used, based on the value of the
symbolelement in the request. - recipientList [line 16 in ESB config] - the
recipientListmediator lists several endpoints inside thesendtags. ESB will forward the request to all endpoints in this list.