Enterprise Integration Patterns
Document Message
This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Document Message EIP can be implemented using the ESB profile of WSO2 EI. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Document Message
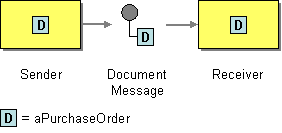
The Document Message EIP is used to reliably transfer a data structure between applications. The Command Message EIP allows you to invoke only a specific client through the ESB, while the Document Message EIP sends the entire data unit to the receiver. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/DocumentMessage.html.
Figure 1: Document Message EIP
Sample scenario
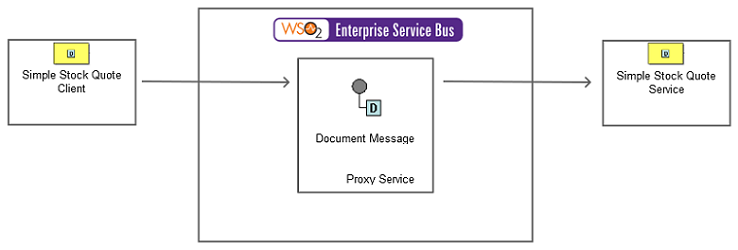
This example demonstrates the ESB profile transmitting an entire message from a client to a sample Axis2 server as a document message, which the Axis2 server processes so it can identify which operation to invoke.
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using the ESB profile.
Figure 2: Example Scenario of the Document Message EIP
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Document Message EIP by comparing their core components.
| Document Message EIP (Figure 1) | Document Message Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Sender | Stock Quote Client |
| Document Message | Proxy Service |
| Receiver | Simple Stock Quote Service Instance |
The ESB Configuration
Given below is the ESB configuration of this sample. Log in to the Management Console of the ESB profile, click Main, and then click Source View in the Service Bus menu to view this.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<proxy name="DocumentMessageProxy" transports="https http" startOnLoad="true" trace="disable">
<target>
<inSequence>
<send>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService" />
</endpoint>
</send>
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send />
</outSequence>
</target>
</proxy>
</definitions>
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the configuration in detail.
- Proxy Service - The proxy service takes requests and forwards them to the back-end service, abstracting the routing logic from the client. In this example scenario, the proxy service just forwards requests to the back-end service following the Document Message EIP style.
Simulating the sample scenario
Now, let's try out the sample scenario explained above.
Setting up the environment
Download the Document-Message.zip, which includes the artifacts of this sample and follow the steps in Simulating a Sample Scenario.
Executing the sample
Using a SOAP client (such as SoapUI), send a request to the ESB server to invoke the DocumentMessageProxy. Note that the entire request will be passed to the back-end Axis2 Server, and the client will receive the response in return.
Request command:
ant stockquote -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:8280/services/DocumentMessageProxy
Stock Quote Client output:
Standard :: Stock price = $72.78678053494932
Axis2 server console output:
samples.services.SimpleStockQuoteService :: Generating quote for : IBM