This site contains the documentation that is relevant to older WSO2 product versions and offerings.
For the latest WSO2 documentation, go to https://wso2.com/documentation/.
Control Bus
This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Control Bus EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Control Bus
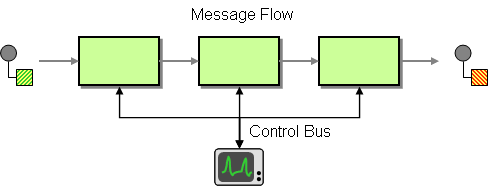
Effective network management is important in distributed networking environments. The Control Bus EIP helps effectively administer a messaging system that is distributed across multiple platforms and a wide geographic area. It uses the same messaging mechanism used by the application data, but separate channels are used to transmit data that is relevant to the management of components involved in the message flow. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/ControlBus.html.
Figure 1: Control Bus EIP
Example scenario
In this example scenario, we use the Throttle mediator of WSO2 ESB to control access through throttling policies. Based on the policy, if the control flow is in order, it will be directed to onAccept. If not, it will be directed to onReject.
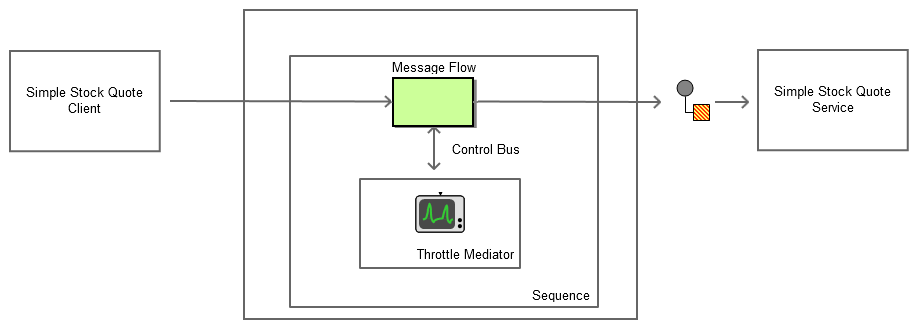
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using WSO2 ESB.
Figure 2: Example Scenario of the Control Bus EIP
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Control Bus EIP by comparing their core components.
| Control Bus EIP (Figure 1) | Control Bus Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Message Flow | Message Flow |
| Control Bus | Throttle Mediator |
Environment setup
- Download and install WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, refer to Getting Started in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Start the sample Axis2 server. For instructions, refer to the section ESB Samples Setup - Starting Sample Back-End Services in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ESB configuration
Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (https://localhost:9443/carbon). In the management console, navigate to the Main menu and click Source View in the Service Bus section. Next, copy and paste the following configuration, which helps you explore the example scenario, to the source view.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<sequence name="fault">
<log level="full">
<property name="MESSAGE" value="Executing default "fault" sequence"/>
<property name="ERROR_CODE" expression="get-property('ERROR_CODE')"/>
<property name="ERROR_MESSAGE" expression="get-property('ERROR_MESSAGE')"/>
</log>
<drop/>
</sequence>
<sequence name="main">
<in>
<throttle id="A">
<policy>
<wsp:Policy xmlns:wsp="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/09/policy"
xmlns:throttle="http://www.wso2.org/products/wso2commons/throttle">
<throttle:ThrottleAssertion>
<throttle:MaximumConcurrentAccess>4</throttle:MaximumConcurrentAccess>
</throttle:ThrottleAssertion>
</wsp:Policy>
</policy>
<onReject>
<log level="custom">
<property name="text" value="Access Denied By Message System"/>
</log>
<makefault>
<code xmlns:tns="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope" value="tns:Receiver"/>
<reason value="Access Denied By Messaging System"/>
</makefault>
<property name="RESPONSE" value="true"/>
<header name="To" action="remove"/>
<send/>
<drop/>
</onReject>
<onAccept>
<log level="custom">
<property name="text" value="Access Granted By Message System"/>
</log>
<send>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</endpoint>
</send>
</onAccept>
</throttle>
</in>
<out>
<throttle id="A"/>
<send/>
</out>
</sequence>
</definitions>
Simulating the sample scenario
Send more than four requests to WSO2 ESB using the Stock Quote client as follows. For information about the Stock Quote client, refer to the Sample Clients section in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ant stockquote -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:8280/ -Dsymbol=foo
If more than four requests are sent simultaneously to the server, all other request will not be accepted. The Control bus regulates the message request flow through throttling.
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below refer to the ESB configuration shown above.
- sequence [line 11 in ESB config] - The main sequence, which is the default in the ESB.
- throttle [line 13 in ESB config] - Defines a throttling policy in WS-Policy.
- WS-Policy Assertion [line 18 in ESB config] - The WS-Policy assertion
throttle:MaximumConcurrentAccessdefines the number of concurrent connections that can be made. - onReject [line 22 in ESB config] - The
onRejectelement of the Throttle mediator defines what to do if the policy is rejected. The maximum number of concurrent connections at present exceeds 4. In this example, if the policy is rejected, the message is logged and a fault is returned to the client usingmakeFaultwith message 'access is denied'. - onAccept [line 35 in ESB config] - The
onAcceptelement of the Throttle mediator defines what to do when the policy is accepted. The maximum number of concurrent connections at present does not exceed 4. In this example, if the policy is accepted, the message is passed on to the service endpoint.