Overview
WSO2 Open Banking is a purpose-built solution for regulatory compliance and supports Consumer Data Standards. WSO2 Open Banking helps align banking and regulatory needs with technology infrastructures and regulatory expertise to quickly satisfy compliance. This documentation explains the following:
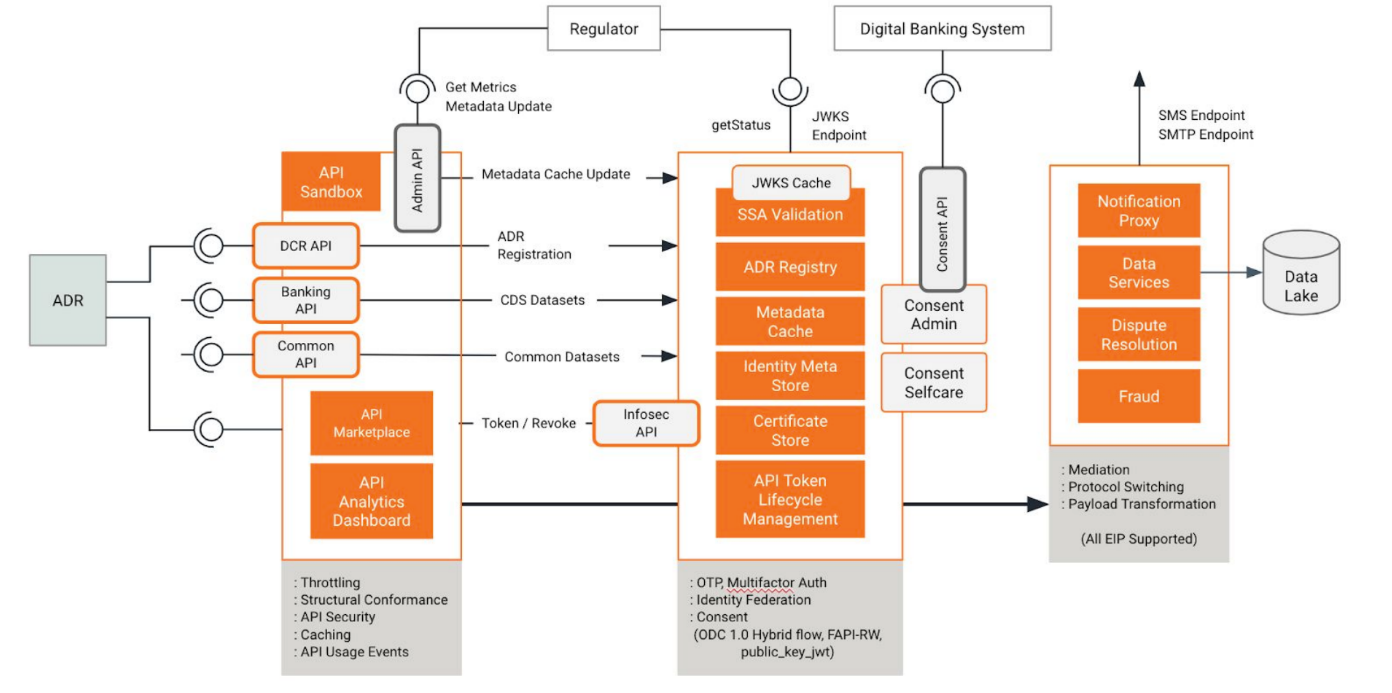
Architecture
WSO2 Open Banking has a technology stack that banks need to become Consumer Data Right compliant and digitally transformed. It is assembled using a componentized architecture ensuring flexibility to meet different technology use cases. Built on top of a unified integration platform. WSO2 Open Banking helps banks become integration agile for any digital initiative beyond compliance.
It leverages five key technology areas critical to a banking infrastructure - API Management, Identity and Access Management, Integration, Analytics and Business Insights, and Fraud Detection bundled together to form a componentized architecture. This gives the flexibility to reuse existing infrastructure, and banks only need to obtain the components that are not available in their current infrastructure.
Modules
WSO2 Open Banking contains the following main modules in the solution:
API Management
The WSO2 Open Banking API management component allows banks to securely expose data to third parties via APIs. This enables banks to grant Data Recipients with access to customers' account data and the ability to initiate payments with the customers' consent. It supports a fully-fledged API lifecycle management functionality along with version management.
API publishers can publish APIs and once the client registration is completed, API consumers can subscribe to published APIs and use them in their banking applications. API Management module supports token validation, scope validation, and fine-grained access control ensure API security that prevents unauthorized API calls.
Identity and Access Management
The WSO2 Open Banking identity and access management component enables comprehensive security mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access to APIs and secured data.
Regulatory Compliance with Consumer Data Right
The Australian Government introduced the Consumer Data Right (CDR) to give consumers more control over their data. CDR provides customers and small businesses a choice about how their data is shared with third parties and sets standards for a whole industry about what data should be made available safely. In doing so, CDR encourages competition between service providers, leading to better prices for customers and more innovative products and services.
The CDR will be rolled out sector-by-sector, starting with the banking sector. Further information on the CDR is available on the Treasury website at https://treasury.gov.au/consumer-data-right.
Specific examples of the benefits of a CDR might include:
- Banking applications that analyse credit card customers spending and repayment behaviours to identify the best product for an individual, saving them money on high fees or obtaining better interest rates.
- Applications that help customers understand and manage their energy use to save money on their power bills.
- Comparison websites that identify a more appropriate internet or mobile phone plan taking into account each customer’s actual usage and budget.
Key Concepts
This section explains the key concepts in open banking. For more details see /wiki/spaces/OB200/pages/48629460.
Consumer Data Right
The Australian Government introduced the Consumer Data Right (CDR) to give consumers more control over their data. CDR provides customers and small businesses a choice about how their data is shared with third parties and sets standards for a whole industry about what data should be made available safely. In doing so, CDR encourages competition between service providers, leading to better prices for customers and more innovative products and services.
The CDR will be rolled out sector-by-sector, starting with the banking sector. Further information on the CDR is available on the Treasury website at https://treasury.gov.au/consumer-data-right.
Consumer Data Right for banking
The government determined that the CDR will first apply to the banking sector, followed by the energy sector and then the telecommunications sector. The introduction of CDR in the banking sector will provide consumers with access to, and the ability to safely transfer, their banking data to trusted parties.
The CDR will be introduced into the banking sector in phases and segments. For more details, see Phases of Data Sharing Obligations.
Open Banking
Open banking has been introduced to make banking a more competitive business. Its main goals are offering greater financial transparency, a shared chance of success for all financial service providers, and more innovative services to the consumers.
The current banking practice involves the customer or merchant to maintain separate relationships with different financial institutions to achieve their financial goals. Open banking introduces a more consolidated experience to the customer by allowing banks to expose their functionality via APIs.
Consumer Data Standards
The Consumer Data Standards (CDS) are the technical standards produced by Data61, which is the Data Standards Body that guides the banks/Data Holders on how to implement the CDR. These standards enable consumers to access and direct the sharing of data about them with third parties flexibly and simply, and in ways that ensure security and trust in how that data is being accessed and used.
Stakeholders
Data Holder
The Data Holder (DH) is the organization that CDR is applied to provide data to the consumer. For example, a bank.
Data Recipient
A Data Recipient (DR) is an accredited party that can request CDR data from a Data Holder with the consent of the consumer.
Consumer
The end-user who is benefited from CDR, the consumer can request the Data Holder to provide data.
ACCC
The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) is the lead regulator for the CDR regime, and it has roles and functions that include:
- Drafting rules to implement and govern the CDR in each sector
- Accrediting entities to receive data
- Managing an online register of accredited data recipients and data holders through Dynamic Client Registration (Client Registration)
- Providing education and guidance on the CDR
- Recommending to government future sectors to be brought within the CDR
- Compliance and enforcement activities
Standards
GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a new legal framework formalized in the European Union (EU) in 2016 and comes into effect from 28, May 2018. GDPR effectively replaces the previously used EU Data Protection Directive (DPD).
FAPI
Financial-grade API (FAPI) is an industry-led specification of JSON data schemas, security and privacy protocols to support use cases in the financial industry and other industries that require higher security. FinTech developers can accelerate secure open banking with FAPI. It uses OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect (OIDC) as its base and defines additional technical requirements.
CPS 234
Cross-industry Prudential Standards 234 Information Security (CPS 234) is a mandatory regulation issued by the Australian Prudential Regulatory Authority (APRA). The APRA regulated entities and the information assets managed by them and associated third parties should comply with CPS 234. WSO2 Open Banking is not an APRA regulated entity, but the solution can be categorized as a third-party provider that provides information assets to regulated entities. For more information on how the solution meets CPS 234, see Prudential Standard CPS 234.
ISO/IEC 27001
ISO/IEC 27001 is the internationally recognised specification for an Information Security Management System (ISMS), and it is one of the most popular standards for information security.
Features
The Consumer Data Standards (CDS) are the technical standards produced by Data61, which is the Data Standards Body that guides the banks/Data Holders on how to implement the Consumer Data Right. These standards enable consumers to access and direct the sharing of data about them with third parties flexibly and simply, and in ways that ensure security and trust in how that data is being accessed and used.
WSO2 Open Banking supports the Australian Consumer Data Standards specification version 1.3.1 that includes the following APIs:
| Available API | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Consumer Data Standards | To retrieve account and transaction details of consumers with their authorisation. |
| Consumer Data Standards Administration API | Allows the ACCC to obtain operational statistics from the Data Holder |
| CDR Arrangement Management API | To inform relevant parties that a particular CDR Arrangement ID/consent is not valid anymore. |
These features are available in WSO2 Open Banking for Australia: