The following scenario expands on two different scenarios where provisioning happens. For both these scenarios, advanced claims are very useful. 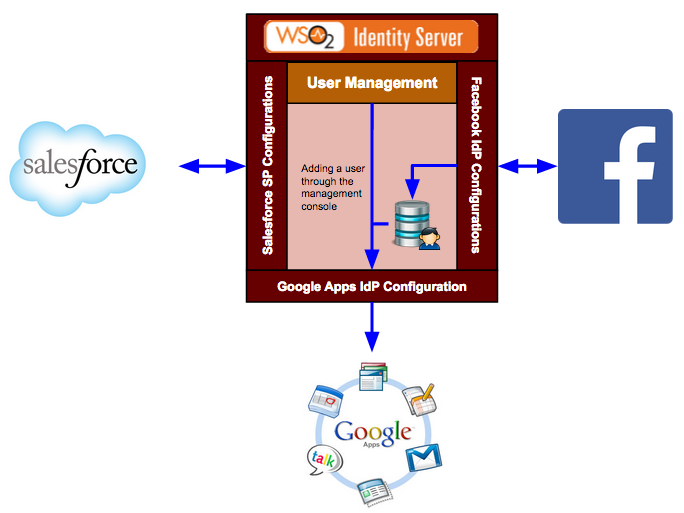
In the above scenario, Google Apps is configured as an identity provider in the Identity Server. When a user is added to the management console of the Identity Server, the user is provisioned to Google Apps using the Google Apps identity provider configuration in the Identity Server. The next scenario is for Just-In-Time (JIT) provisioning. Salesforce is the service provider and Facebook is the identity provider configured in the Identity Server. When JIT provisioning is configured the user is provisioned to the user store configured in the Identity Server. If the same user store is configured in the Google Apps identity provider configuration and JIT provisioning is enabled, the user is provisioned there as well. JIT provisioning happens while in the middle of an authentication flow. The provisioning can happen in a blocking mode or in a non-blocking mode. In the blocking mode, the authentication flow will be blocked until the provisioning finishes - while in the non-blocking mode, provisioning happens in a different thread. In both these scenarios, only some specific user attributes must be configured for provisioning as the claims are different for both Facebook and Google Apps and also for the Identity Server and Google Apps. |