This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Datatype Channel EIP can be implemented using the WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
| Table of Contents |
|---|
...
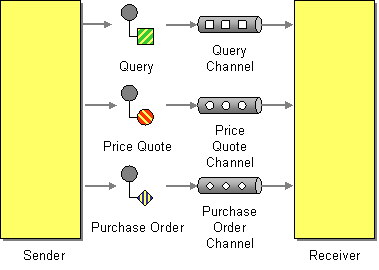
This EIP creates a separate channel for each type of data so that all the messages on a given channel will contain the same data type. The sender, who knows the data type, should select the appropriate channel on which to send the message. The receiver knows which identifies the type of data a message contains, based on the channel in which it is received.
For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/DatatypeChannel.htmlgo to Data Type Channel.
Figure 1: Datatype Channel EIP
Example scenario
...
This example scenario depicts
...
a Stock Quote
...
service deployed in Axis2 server. It offers several service operations to the user.
...
The ESB uses the filter mediator to identify each action that is specified by the sender and diverts the request into the appropriate sequence. Each sequence acts as a separate channel. The sender experiences the decomposition of channels through a log message indicated by
...
the ESB. There will be a different log message for each operation the sender requests.
The following diagram
...
depicts how
...
this example scenario
...
can be depicted using the ESB.
Figure 2: Example Scenario scenario of the Datatype Channel EIP
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Datatype Channel EIP by comparing their core components.
| Datatype Channel EIP (Figure 1) | Datatype Channel Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Sender | Client |
| Datatype Channel |
the ESB. | |
| Receiver | Stock Quote |
Environment setup
- Download and install WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, refer to Getting Started in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Deploy the
SimpleStockQuoteServiceby starting the Sample Axis2 server on port 9000. For instructions, refer to the section ESB Samples Setup - Starting Sample Back-End Services in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ESB configuration
...
| Service |
The ESB configuration
Given below is the ESB configuration for simulating the example scenario explained above.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Code Block | |
|---|---|
| language | html/xml | linenumbers | true
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse"> <endpoint name="StockQuoteReceiver"> <address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/> </endpoint> <sequence name="MarketActivity"> <in> <log level="custom"> <property name="MessaginMessaging_Channel" value="MARKET_ACTIVITY"/> </log> <send> <endpoint key="StockQuoteReceiver"/> </send> </in> <out> <send/> </out> </sequence> <sequence name="FullQuote"> <in> <log level="custom"> <property name="MessaginMessaging_Channel" value="FULL_QUOTE"/> </log> <send> <endpoint key="StockQuoteReceiver"/> </send> </in> <out> <send/> </out></sequence> </sequence> <sequence name="faultStockQuote"> <log level="fullcustom"> <property name="MESSAGE" value="Executing default "fault" sequence"/> <property name="ERRORMessaging_CODEChannel" expressionvalue="get-property('ERROR_CODE')STOCK_QUOTE"/> <property name="ERROR_MESSAGE" expression="get-property('ERROR_MESSAGE')"/></log> </log> <send> <drop/> </sequence> <endpoint <sequence namekey="StockQuoteStockQuoteReceiver"/> <in> </send> </sequence> <proxy <log levelname="customdatatype-channel-proxy"> <property name="Messagin_Channel" value="STOCK_QUOTE"/ startOnLoad="true" transports="http https"> <target> </log> <send> <endpoint key="StockQuoteReceiver"<log/> </send> <inSequence> </in> <out> <send/> </out> </sequence> <sequence name="main"> <switch source="get-property('Action')"> <log/> <in> <filter source="get-property('Action')"<case regex="/*urn:getQuote/*"> <then> <sequence key="StockQuote"/> </then> <else/></case> </filter> <filter source="get-property('Action')" <case regex="/*urn:getFullQuote/*"> <then> <sequence key="FullQuote"/> </then> <else/></case> </filter> <filter source="get-property('Action')" <case regex="/*urn:getMarketActivity/*"> <then> <sequence key="MarketActivity"/> </then>case> <else</>switch> </filter>inSequence> </in> <outSequence> <out> <send<respond/> </out>outSequence> </target> </sequence>proxy> </definitions> |
Simulating the sample scenario
- Send a request using the
Stock Quoteclient to WSO2 ESB in the following manner. For information about the Stock Quote client, refer to the section Sample Clients in the WSO2 ESB documentation.ant stockquote -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:8280/ -Dmode=quote - Also execute the command above with
-Dmode=[quote | marketactivity | fullquote], and observe the ESB's log of the corresponding valuesSTOCK_QUOTE,MARKET_ACTIVITYandFULL_QUOTE.
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below are mapped with the ESB configuration shown above.
...
| Excerpt | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
The configuration elements The elements used in the above ESB configuration are explained below.
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
Simulating the example scenario
Now, let's try out the example scenario explained above.
Setting up the environment
You need to set up the ESB, and the back-end service:
- Download the
Datatype_1.0.0.zipfile, which includes the ESB configuration described above. See Setting up the Environment for instructions on setting up the ESB and the back-end service.
Info When you set up the environment, note that you only need to start one instance of the back-end service (Stock Quote Service) to simulate this example.
Executing the sample
Let's send a request to the ESB using the Stock Quote Client application. Find out more about the Stock Quote Client from the ESB documentation.
- Open a new terminal, and navigate to the
<ESB_HOME>/samples/axis2Client/directory. The Stock Quote client application is stored in this directory. Execute the following command to send the request to the ESB.
Code Block ant stockquote -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:8280/services/datatype-channel-proxy -Dmode=quote
Analyzing the output
When you execute the command above, the ESB first receives the message and then routes it to the back-end service (StockQuoteService). The following output will be printed on the Axis2 server's console:
Stock Client Console output :
Standard :: Stock price = $172.81050109499768
Axis2 server console output:
samples.services.SimpleStockQuoteService :: Generating quote for : IBM
ESB Profile logs:
INFO - LogMediator Messaging_Channel = STOCK_QUOTE
Also execute the below commands, and observe the ESB profile log of the corresponding values: STOCK_QUOTE, MARKET_ACTIVITY and FULL_QUOTE.
- ant stockquote -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:8280/services/datatype-channel-proxy -Dmode=marketactivity
ant stockquote -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:8280/services/datatype-channel-proxy -Dmode=fullquote
Notice the following respective output.
Stock Client Console output :
Activity :: Average price = $123.67485145988432
Full :: Average price = $125.67875616729333
Axis2 server console output:
- samples.services.SimpleStockQuoteService :: Generating Market activity report for : [JLN, FDZ, EQR, XNV, RDR, CZC, LIY, ZEP, ZJX, GWO, STS, NQU, RMA, UUR, PFL, ZEF, IYU, ZLV, KTW, PUN, IOZ, PZJ, HAE, PSL, CQM, CLX, BWI, UYF, QWC, EKB, LMM, UQI, GZA, KRC, GFB, DWM, ETA, SRS, VEP, ZTS, TNE, FJF, LNV, QBY, ZIO, HBS, IIW, SNO, MMO, BTY, OGJ, OUW, CLW, OZT, MXB, HNK, FQC, VEI, BLD, LUP, PHR, JUQ, MZM, GIL, EVE, UAH, SHV, WYS, MAG, XBX, ZYB, MUX, MUO, DAM, DVR, RDF, LGB, KGS, DWP, ZAG, SDF, BSF, CTX, MKG, YTO, RRX, OVJ, MEZ, ODU, JGU, GQB, SLW, UCQ, GDI, DIO, BKV, UUQ, JES, TAZ, AAU]
samples.services.SimpleStockQuoteService :: Full quote for : IBM
ESB Profile logs:
INFO - LogMediator Messaging_Channel = MARKET_ACTIVITY
INFO - LogMediator Messaging_Channel = FULL_QUOTE