This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Message Endpoint EIP can be implemented using the WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Message Endpoint
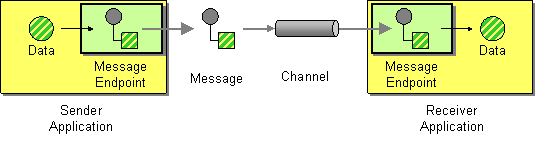
The Message Endpoint EIP encapsulates the messaging system inside an application. It then customizes a general messaging API for a specific application and task. Therefore, you can change the message API just by changing the endpoint code. This improves the maintainability of applications.
For more information, go to Message Endpoint.
Figure 1: Message Endpoint EIP
Example scenario
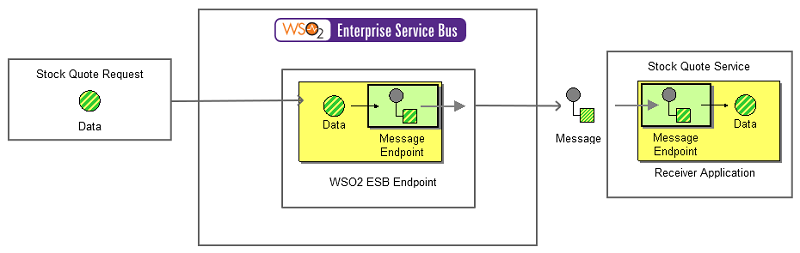
The example scenario is an inventory for stocks. It illustrates how a stock quote is generated when a request is sent to the ESB. The sender sends the request to the ESB, where the request is then diverted to the stock quote service. The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using the ESB.
Figure 2: Example scenario of the Message Endpoint EIP
Before digging into the implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Message Endpoint EIP by comparing their core components.
| Message Endpoint EIP (Figure 1) | Message Endpoint Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
Data | Stock Quote Request |
Message Endpoint | WSO2 ESB |
Receiver Application | Stock Quote service |
The ESB configuration
Given below is the ESB configuration for simulating the example scenario explained above.
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<!-- Will trigger when the message is sent to message-endpoint-proxy -->
<proxy name="message-endpoint-proxy" startOnLoad="true" transports="http https">
<target>
<inSequence>
<!-- Sends the message to the specified service -->
<send>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</endpoint>
</send>
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<respond/>
</outSequence>
</target>
</proxy>
</definitions>
The configuration elements
The elements used in the above ESB configuration are explained below.
- <proxy> - This is the proxy service that should be invoked to execute the configuration.
- <inSequence> - A message is first received by the proxy service, and then directed to this sequence.
- <endpoint> - The destination to which the message will be sent.
- <outSequence> - This sequence is triggered after the execution of the <inSequence>.
Simulating the example scenario
Now, let's try out the example scenario explained above.
Setting up the environment
You need to set up the ESB, and the back-end service:
- Download the
Message-Endpoint.zipfile, which includes the ESB configuration described above. - See Setting up the Environment for instructions on setting up the ESB and the back-end service.
Executing the sample
Send the following request to the ESB, by using a SOAP client:
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:ser="http://services.samples" xmlns:xsd="http://services.samples/xsd">
<soapenv:Header/>
<soapenv:Body>
<ser:getQuote>
<ser:request>
<xsd:symbol>foo</xsd:symbol>
</ser:request>
</ser:getQuote>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope>
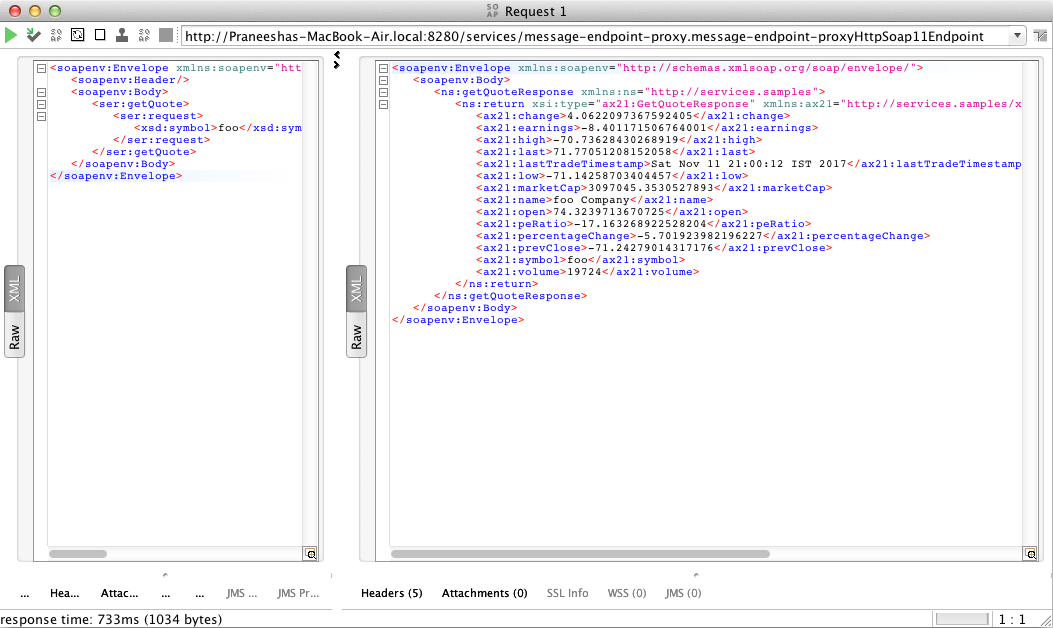
Analyzing the output
When you send the request, the ESB first receives the message and then routes it to the back-end service (StockQuoteService). The following output will be printed on the Axis2 server's console, confirming that the request is successfully received by the back-end service.
samples.services.SimpleStockQuoteService :: Generating quote for : foo
You can view the response in the SOAP UI as follows: