This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Test Message EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Test Message
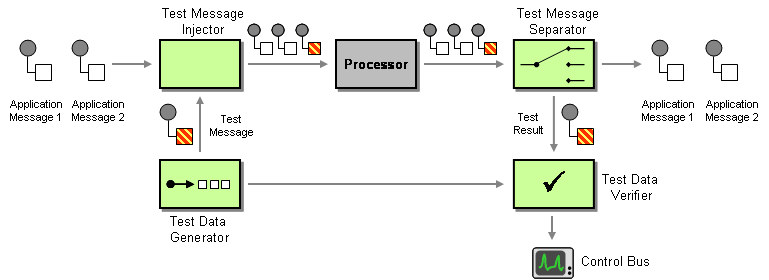
The Test Message EIP ensures the health of message processing components by preventing situations such as garbling outgoing messages due to an internal fault. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/TestMessage.html.
Figure 1: Test Message EIP
Example scenario
This example scenario demonstrates how to send a test message and determine the availability of a service. You can also see how the Scheduled Tasks in WSO2 ESB are used.
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using the WSO2 ESB.
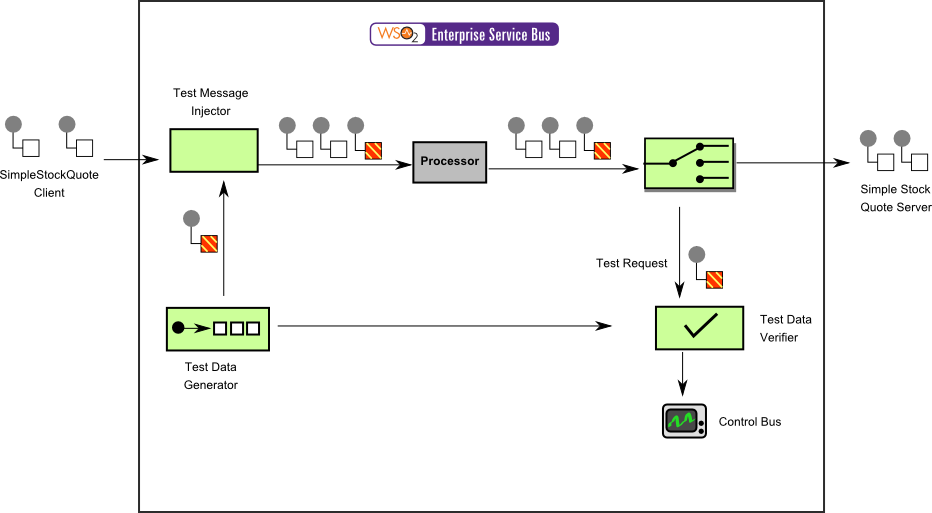
Figure 2: Example Scenario of the Test Message EIP
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Detour EIP by comparing their core components.
| Test Message EIP (Figure 1) | Example Scenario of the Test Message EIP (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Application Messages | Simple Stock Quote Client |
| Test Data Generator | Test data generator role is played by the Task Scheduler in the ESB. It creates a message after a given interval and hands over the message to the main sequence. |
| Test Message Injector | Main sequence injects messages it gets from Task scheduler into sendSeq, where the rest of the messages go. |
| Test Message Separator and Test Data Verifier | A Filter mediator inside receiveSeq filters out the test messages and prints the outcome of the test. There's another filter in fault c to monitor any failures in sending test messages. |
Environment setup
- Download and install WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, refer to Getting Started in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Start a sample Axis2 server instance on port 9000. For instructions, see ESB Samples Setup - Starting Sample Back-End Services in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ESB configuration
Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (https://localhost:9443/carbon). In the management console, navigate to the Main menu and click Source View in the Service Bus section. Next, copy and paste the following configuration, which helps you explore the example scenario, to the source view.
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<!-- Proxy for normal message flow -->
<proxy name="ServiceProxy" transports="https http" startOnLoad="true" trace="disable">
<target inSequence="sendSeq"/>
</proxy>
<!-- Normal flow of the messages -->
<sequence name="sendSeq">
<send receive="receiveSeq">
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</endpoint>
</send>
</sequence>
<!-- Fault sequence handles failures -->
<sequence name="fault">
<log level="full">
<property name="MESSAGE" value="Executing default 'fault' sequence"/>
<property xmlns:ns="http://org.apache.synapse/xsd"
name="ERROR_CODE"
expression="get-property('ERROR_CODE')"/>
<property xmlns:ns="http://org.apache.synapse/xsd"
name="ERROR_MESSAGE"
expression="get-property('ERROR_MESSAGE')"/>
</log>
<!-- Filter the failed Test Messages -->
<filter xmlns:ns="http://org.apache.synapse/xsd"
xmlns:m0="http://services.samples"
source="//m0:getQuote/m0:request/m0:symbol"
regex="TEST">
<then>
<log>
<property name="FAILURE" value="*** Test Message Failed ***"/>
<property name="FAILED SERVICE" value="*** localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService ***"/>
</log>
</then>
<else/>
</filter>
<drop/>
</sequence>
<!-- Receiving messages from service -->
<sequence name="receiveSeq">
<log/>
<!-- Filter the Test Messages -->
<filter xmlns:ax21="http://services.samples/xsd"
xmlns:ns="http://org.apache.synapse/xsd"
source="//ax21:symbol"
regex="TEST">
<then>
<log>
<property name="TEST PASSED" value="*** Test Message Passed ***"/>
<property name="TESTED SERVICE" value="*** localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService ***"/>
</log>
<drop/>
</then>
<else>
<send/>
</else>
</filter>
</sequence>
<!-- main sequence used as the test Message injector -->
<sequence name="main">
<in>
<sequence key="sendSeq"/>
</in>
<out>
<send/>
</out>
</sequence>
<!-- Task Scheduler act as Test data generator -->
<task name="Testing"
class="org.apache.synapse.startup.tasks.MessageInjector"
group="synapse.simple.quartz">
<!-- Interval between generating test messages, Cron Expression are also allowed to use -->
<trigger interval="25"/>
<property xmlns:task="http://www.wso2.org/products/wso2commons/tasks" name="message">
<m0:getQuote xmlns:m0="http://services.samples">
<m0:request>
<m0:symbol>TEST</m0:symbol>
</m0:request>
</m0:getQuote>
</property>
<property xmlns:task="http://www.wso2.org/products/wso2commons/tasks"
name="soapAction"
value="urn:getQuote"/>
<property xmlns:task="http://www.wso2.org/products/wso2commons/tasks"
name="to"
value="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</task>
</definitions>
Simulating the sample scenario
After setting this configuration, note that the Axis2 server is invoked every 25 seconds, and the following message on the WSO2 ESB console indicates that the test has passed.
INFO - LogMediator To: http://www.w3.org/2005/08/addressing/anonymous, WSAction: , SOAPAction: , MessageID: urn:uuid:fa29b7c1-98cb-48a2-87b3-54dc96b9c817, Direction: response, TEST PASSED = *** Test Message Passed ***, TESTED SERVICE = *** localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService ***
If you stop the Axis2 server, you will get the following message indicating that the test has failed.
INFO - LogMediator To: http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService, WSAction: urn:getQuote, SOAPAction: urn:getQuote, MessageID: urn:uuid:008c1cf5-a13b-44ec-8e1c-566a39275f67, Direction: request, FAILURE = *** Test Message Failed ***, FAILED SERVICE = *** localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService ***
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below refer to the ESB configuration shown above.
- sequence [line 8 in ESB config] - The sequence with key
sendSeqdefines the endpoint where messages will be sent and defines the sequence (receiveSeq) that will receive responses. - fault sequence [line 17 in ESB config] - The fault sequence provides a channel for handling faults.
- filter [line 29 in ESB config] - A filter mediator is used within the fault sequence to determine whether the symbol property of the message passing through this filter contains
TEST. If it does, it will be logged, and no fault message is passed onto the requesting client. IfTESTdoes not exist, a fault message is passed as usual. - sequence [line 66 in ESB config] - This is the main sequence invoked by default when a request is made to the ESB. This sequence calls the
sendSeqsequence (line 8 in ESB config). - task [line 76 in ESB config] - A task in the ESB runs periodically based on a given timer. This timer is specified using the trigger element. In this case, the task is set to run every 25 seconds. This task uses the Synapse
MessageInjectorclass to inject a message into the Synapse environment. - property [line 83 in ESB config] - This property, defined inside the task, specifies the message body.
- property [line 90 in ESB config] - This property, defined inside the task, sets the SOAP Action to
getQuote. - property [line 93 in ESB config] - This property, defined inside the task, specifies the address where the message generated by the task is sent.