This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Selective Consumer EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Selective Consumer
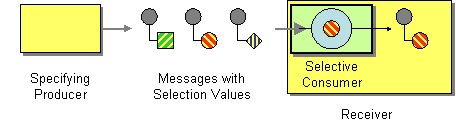
The Selective Consumer EIP allows a message consumer select which messages it wishes to receive. It filteres the messages delivered by its channel so that it only receives the ones that match its criteria. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/MessageSelector.html.
Figure 1: Selective Consumer EIP
Example scenario
This example scenario demonstrates how a specific receiver only processes messages that are pre-filtered based on certain criteria. We have an Axis2 server as the consumer. The consumer criteria is specified through an XML schema validation, which is stored as a local entry in the registry. We use the Validate mediator to check whether the messages that are sent to the ESB match the criteria of the schema. The Axis2 server can consume the message only if the message meets the validation criteria.
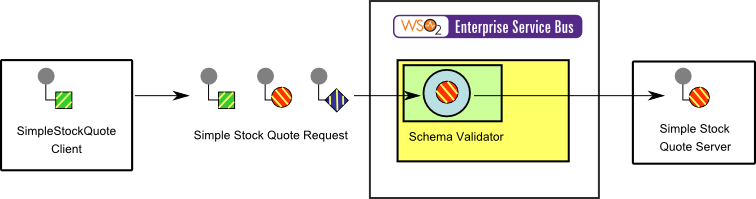
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using WSO2 ESB.
Figure 2: Example Scenario of the Selective Consumer EIP
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Selective Consumer EIP by comparing their core components.
| Figure 1: Selective Consumer EIP | Figure 2: Selective Consumer Example Scenario |
|---|---|
| Specifying Producer | Simple Stock Quote Client |
| Messages with Selection Values | Simple Stock Quote Request |
| Selective Consumer | Schema Validator (Validate Mediator) |
| Receiver | Simple Stock Quote Server |
Environment setup
- Download an install the WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, refer to Getting Started in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Start the sample Axis2 server. For instructions, refer to section ESB Samples Setup - Starting Sample Back-End Services in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ESB configuration
Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (https://localhost:9443/carbon). In the management console, navigate to Main Menu, click Service Bus and then Source View. Next, copy and paste the following configuration, which helps you explore the example scenario, to the source view.
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<localEntry key="selective_criteria">
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns="http://www.apache-synapse.org/test"
elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified"
targetNamespace="http://services.samples">
<xs:element name="getQuote">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="request">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="stockvalue" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
</localEntry>
<sequence name="fault">
<log level="full">
<property name="MESSAGE" value="Executing default "fault" sequence"/>
<property name="ERROR_CODE" expression="get-property('ERROR_CODE')"/>
<property name="ERROR_MESSAGE" expression="get-property('ERROR_MESSAGE')"/>
</log>
<drop/>
</sequence>
<sequence name="main">
<in>
<validate>
<schema key="selective_criteria"/>
<on-fail>
<makefault>
<code xmlns:tns="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope" value="tns:Receiver"/>
<reason value="Invalid custom quote request"/>
</makefault>
<property name="RESPONSE" value="true"/>
<header name="To" expression="get-property('ReplyTo')"/>
<drop/>
</on-fail>
</validate>
<send>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService?wsdl"/>
</endpoint>
</send>
</in>
<out>
<send/>
</out>
</sequence>
</definitions>
Simulating the sample scenario
Send the following request using a client like SOAP UI.
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:ser="http://services.samples" xmlns:xsd="http://services.samples/xsd">
<soapenv:Header/>
<soapenv:Body>
<ser:getQuote>
<!--Optional:-->
<ser:request>
<!--Optional:-->
<ser:symbol>IBM</ser:symbol>
</ser:request>
</ser:getQuote>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope>
Note that the stock quote request is not processed. Send the following message to the ESB server.
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:ser="http://services.samples" xmlns:xsd="http://services.samples/xsd">
<soapenv:Header/>
<soapenv:Body>
<ser:getQuote>
<!--Optional:-->
<ser:request>
<!--Optional:-->
<ser:stockvalue></ser:stockvalue>
</ser:request>
</ser:getQuote>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope>
The consumer has specified the criteria of using a schema validation. Only the messages that meet this criteria will be consumed.
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below refer to the ESB configuration in step 3 above.
- localEntry [line 3 in ESB config] - A local registry entry with key
selective_criteriais used to define the XML schema used for validation inside the main sequence. - validate [line 34] in ESB config] - This mediator is used to define the portion of a message used for validation. In this example, no source attribute is specified using an XPath expression. It makes the ESB perform the validation on the first child of the SOAP body.
- scehma [line 35 in ESB config] - Defines which schema to use for validation. In this example, the local registry entry definition in line 3 is used.
- on-fail [line 36 in ESB config] - Defines what is to be carried out on failure of a validation. In this example, a fault is created and the message is dropped.