This site contains the documentation that is relevant to older WSO2 product versions and offerings.
For the latest WSO2 documentation, go to https://wso2.com/documentation/.
Scatter-Gather
This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Scatter-Gather EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Scatter-Gather
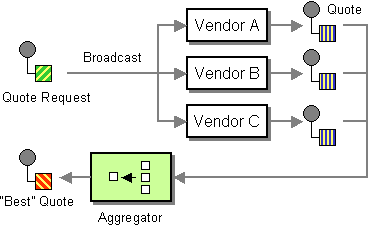
The Scatter-Gather EIP maintains the overall message flow when a message needs to be sent to multiple recipients, each of which may send a reply back. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/BroadcastAggregate.html.
Figure 1: Scatter-Gather EIP
Example scenario
This example scenario demonstrates an implementation of Scatter-Gather EIP that broadcasts a message to multiple recipients using WSO2 ESB. The ESB uses the Aggregate mediator to collect the responses and merge them into a single response message.
We use a sample Stock Quote service as the service provided by the vendors. In this scenario, you send a quote request to three vendors, get quotes for certain items, and return the best quote to the client. We assume that all three vendors implement the same service contract. If the service contracts are different, the ESB must transform the messages before sending them to the vendor services and then transform the responses before returning them to the client. The XSLT mediator is designed to handle these transformations.
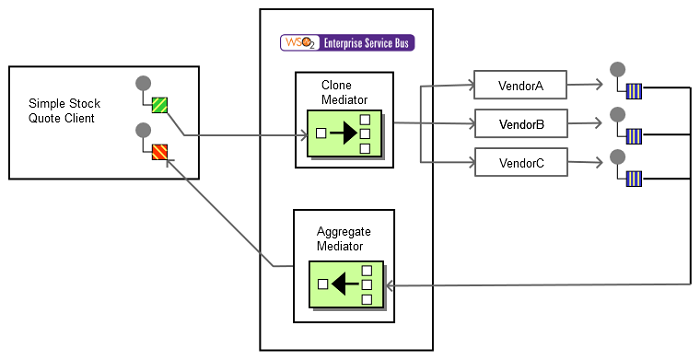
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using WSO2 ESB.
Figure 2: Scatter-Gather Example Scenario
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Scatter-Gather EIP by comparing their core components.
| Scatter-Gather EIP (Figure 1) | Scatter-Gather Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Quote Request | Simple Stock Quote Request |
| Broadcast | |
| Quote | Simple Stock Quote Service Response |
| Aggregator | Aggregate Mediator |
| Best Quote | Aggregated Response |
Environment setup
- Download and install WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, refer to Installation Guide in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Start three sample Axis2 server instances on ports 9000, 9001, and 9002. For instructions, refer to the section Setting Upp the ESB Samples - Starting the Axis2 server in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ESB configuration
Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (https: //localhost:9443/carbon
). In the management console, navigate to Main -> Services -> Add and then click Proxy Service. Next, copy and paste the following configuration, which helps you explore the example scenario, to a new Pass Through Proxy Service named ScatterGatherProxy.
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<proxy xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse" name="ScatterGatherProxy" transports="https http" startOnLoad="true" trace="disable">
<description/>
<target>
<inSequence>
<clone>
<target>
<endpoint name="vendorA">
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService/"/>
</endpoint>
</target>
<target>
<endpoint name="vendorB">
<address uri="http://localhost:9001/services/SimpleStockQuoteService/"/>
</endpoint>
</target>
<target>
<endpoint name="vendorC">
<address uri="http://localhost:9002/services/SimpleStockQuoteService/"/>
</endpoint>
</target>
</clone>
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<log level="full"/>
<aggregate>
<completeCondition>
<messageCount min="3"/>
</completeCondition>
<onComplete xmlns:m1="http://services.samples/xsd" xmlns:m0="http://services.samples" expression="//m0:return">
<enrich>
<source xmlns:m1="http://services.samples/xsd" clone="true" xpath="//m0:return[not(preceding-sibling::m0:return/m1:last <= m1:last) and not(following-sibling::m0:return/m1:last < m1:last)]"/>
<target type="body"/>
</enrich>
<send/>
</onComplete>
</aggregate>
</outSequence>
</target>
</proxy>
</definitions>
Simulating the sample scenario
Use a SOAP client like SoapUI to send the following request to the
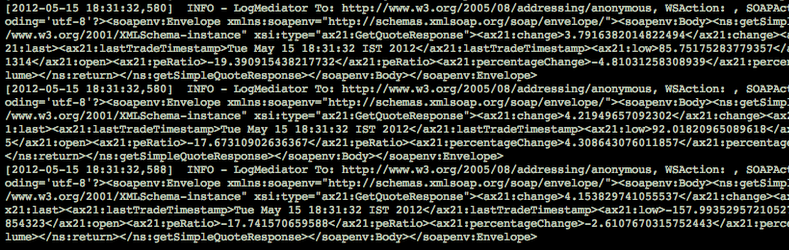
ScatterGatherProxyservice.<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:ser="http://services.samples"> <soapenv:Header/> <soapenv:Body> <ser:getSimpleQuote> <ser:symbol>foo</ser:symbol> </ser:getSimpleQuote> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope>- Because the log mediator is enabled inside the outSequence, there will be three responses from the three vendors. The logs will be similar to the following:
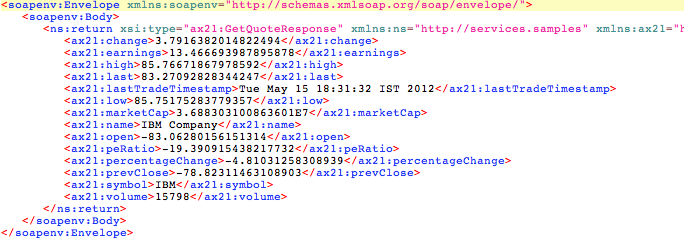
- In SoapUI, you will get the response from the vendor providing the best quote as follows:
- Compare the logged response messages with the response received by the client to see that the
ScatterGatherProxyservice returns the best quote to the client.
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below are mapped with the ESB configuration shown above.
- clone [line 8 in ESB config] - In the
inSequenceof theScatterGatherProxyservice, we use the Clone mediator to make three copies of the request. Those requests are then forwarded to the three vendor services (SimpleStockeQuoteService). The responses to those three requests are received at theoutSequence. The Clone mediator is similar to the Splitter EIP. It clones the incoming request and passes the requests in parallel to several endpoints. - log [line 27 in ESB config] - All received responses are logged before the Aggregate mediator merges them.
- aggregate [line 28 in ESB config] - The Aggregate mediator aggregates response messages for requests made by the Iterate or Clone mediator. The completion condition specifies the minimum or maximum number of messages to be collected.
- onComplete [line 32 in ESB config] - When all messages are aggregated, the
onCompletesequence of the Aggregate mediator will run. This sequence is called once all responses are received or the specified completion condition is met. The responses are aggregated based on the value of thereturnelement in the response. - enrich [line 34 in ESB config] - The Enrich mediator is used to extract the response, which contains the best quote. The following XPath 1.0 expression is used for this purpose:
//m0:return[not(preceding-sibling::m0:return/m1:last <= m1:last) and not(following-sibling::m0:return/m1:last < m1:last)]
In essence, this expression instructs the ESB to pick the response that has the lowestlastvalue. (The XPath 2.0minfunction could reduce the complexity of the above expression, but XPath 1.0 is the current default supported by WSO2 ESB.) Once the proper response is found, we enrich the SOAP body with it and send that response back to the client.