Enterprise Integration Patterns
Service Activator
This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Service Activator EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Service Activator
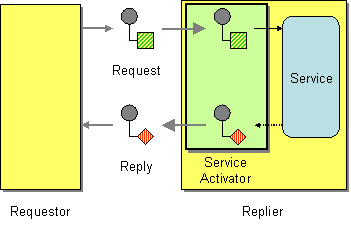
The Service Activator EIP allows an application to design a service to be invoked both via various messaging technologies and non-messaging techniques. Service Activator interfaces methods and services in the back-end service layer so that the back-end services can be filtered and displayed to the client. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/MessagingAdapter.html.
Figure 1: Service Activator EIP
Example scenario
This example scenario demonstrates how WSO2 ESB can be used to activate only a specific number of services on a back-end Axis2 server. Using the publishWSDL property, the service WSDL file is modified to filter out only a specific number of services. The ability of the ESB to create proxy services allows the client to invoke the ESB proxy instead of invoking the service directly on the Axis2 server.
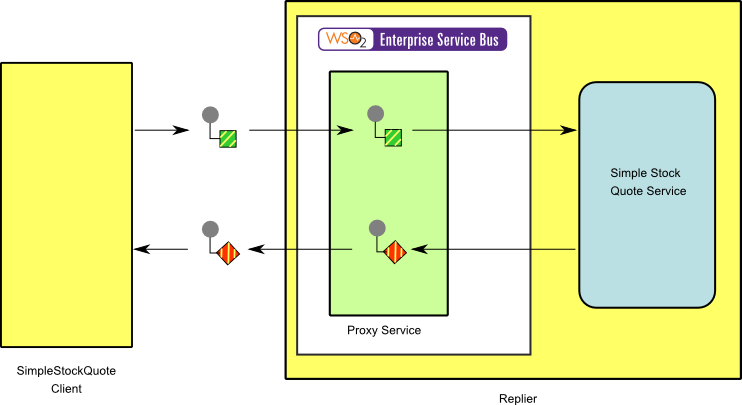
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using WSO2 ESB.
Figure 2: Example Scenario of the Service Activator EIP
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Service Activator EIP by comparing their core components.
| Service Activator EIP (Figure 1) | Service Activator Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Requestor | Simple Stock Quote Client |
| Service Activator | Proxy Service |
| Replier | Simple Stock Quote Service |
Environment setup
- Download and install WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, refer to Installation Guide in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Start two Sample Axis2 server instances in ports 9001 and 9002. For instructions, refer to the section Setting Up the ESB Samples - Starting the Axis2 server in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ESB configuration
Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (https://localhost:9443/carbon). In the management console, navigate to the Main menu and click Source View in the Service Bus section . Next, copy and paste the following configuration, which helps you explore the example scenario, to the source view.
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<proxy name="ServiceActivatorProxy" startOnLoad="true">
<target>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</endpoint>
<outSequence>
<send/>
</outSequence>
</target>
<publishWSDL uri="file:repository/samples/resources/proxy/sample_proxy_1.wsdl"/>
</proxy>
<sequence name="fault">
<log level="full">
<property name="MESSAGE" value="Executing default "fault" sequence"/>
<property name="ERROR_CODE" expression="get-property('ERROR_CODE')"/>
<property name="ERROR_MESSAGE" expression="get-property('ERROR_MESSAGE')"/>
</log>
<drop/>
</sequence>
<sequence name="main">
<in/>
<out>
<send/>
</out>
</sequence>
</definitions>
Simulating the sample scenario
The back-end service StockQuoteService offers the following services:
- getFullQuote
- getMarketActivity
- getQuote
- getSimpleQuote
- placeOrder
Only some of the back-end features will be published through the Service Activator Proxy. Browse http://localhost:8280/services to view the services offered through the ServiceActivatorProxy, and note that services getMarketActivity and getSimpleQuote are not available. Others are available and active.
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below refer to the ESB configuration shown above.
- Proxy [line 2 in ESB config] - The proxy service creates a virtual service between the real back-end service and a requestor.
- publishWSDL [line 11 in ESB config] - By default, a proxy service defines a one-to-one mapping of the back-end service interface in the form of a WSDL file that requestors can use to connect to the proxy service. By using the publishWSDL mediator, the proxy service can publish a custom interface. In this example, the publishWSDL mediator is used to provide access only to a subset of all the service methods available to the back-end service.