The content in this documentation is for older versions of WSO2 products. For updated information on Enterprise Integration Patterns, go to the latest Micro Integrator documentation.
Messaging Bridge
This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Message Bridge EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Messaging Bridge
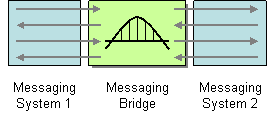
The Messaging Bridge EIP facilitates the connection between messaging systems and replicates messages between them by transforming message formats from one system to the other. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/MessagingBridge.html.
Figure 1: Messaging Bridge EIP
Example scenario
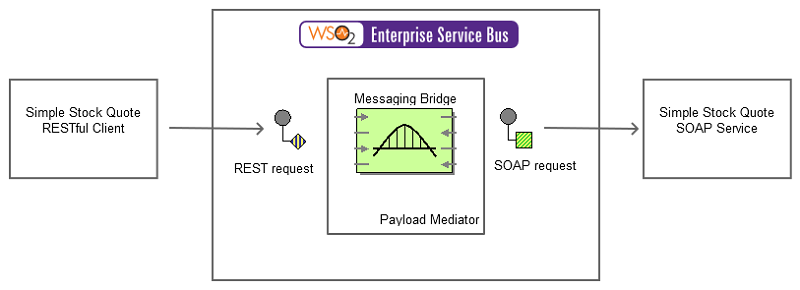
An enterprise might use more than one messaging system in communication. This example illustrates the ESB as a message bridge, which accepts a REST message from the client, transforms the REST message to SOAP format, and sends the SOAP message to the back-end Axis2 server. To transform the sent REST request to a SOAP message, we use the API functionality of the ESB. It restructures the message to a REST format using the WSO2 payload factory mediator.
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using the WSO2 ESB.
Figure 2: Example Scenario of the Messaging Bridge EIP
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Messaging Bridge EIP by comparing their core components.
| Messaging Bridge EIP (Figure 1) | Messaging Bridge Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Messaging System1 | Stock Quote client |
| Messaging Bridge | PayloadFactory Mediator (You can add any transformation mediator here. Also see Message Translator) |
| Messaging System2 | Stock Quote service |
Environment setup
- Download and install WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, refer to Installation Guide in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Start the sample Axis2 server. For instructions, refer to the section Setting Up the ESB Samples - Starting the Axis2 server in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ESB configuration
Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (https://localhost:9443/carbon). In the management console, navigate to the Main menu and click Source View in the Service Bus section. Next, copy and paste the following configuration, which helps you explore the example scenario, to the source view.
<!-- Message Translator-->
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<api name="MessageTranslate" context="/stockquote">
<resource methods="GET" uri-template="/view/{symbol}">
<inSequence>
<payloadFactory>
<format>
<m0:getQuote xmlns:m0="http://services.samples">
<m0:request>
<m0:symbol>$1</m0:symbol>
</m0:request>
</m0:getQuote>
</format>
<args>
<arg expression="get-property('uri.var.symbol')"/>
</args>
</payloadFactory>
<property name="SOAPAction" value="getQuote" scope="transport"></property>
<send>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService" format="soap11"/>
</endpoint>
</send>
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send/>
</outSequence>
</resource>
</api>
</definitions>
Simulating the sample scenario
- Pass the following request to the ESB using the cURL client.
curl -v http://127.0.0.1:8280/stockquote/view/IBM
You can use TCPMon to see the type of the message and its message format:
GET /stockquote/view/IBM HTTP/1.1 User-Agent: curl/7.22.0 (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu) libcurl/7.22.0 OpenSSL/1.0.1 zlib/1.2.3.4 libidn/1.23 librtmp/2.3 Host: 127.0.0.1:8281 Accept: */*
- After sending the request, notice that the Axis2 server has logged the message and accepted the request.
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below are mapped with the ESB configuration shown above.
- Payload Factory [line 6 in ESB config] - Builds the necessary SOAP request for the back-end service. It uses the value of the HTTP GET variable (from the REST request made to the ESB).
- args - [line 14 in ESB config] A list of arguments that will be concatenated in the same order inside the format tags (in a printf style).