The content in this documentation is for older versions of WSO2 products. For updated information on Enterprise Integration Patterns, go to the latest Micro Integrator documentation.
Return Address
This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Return Address Message EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Return Address
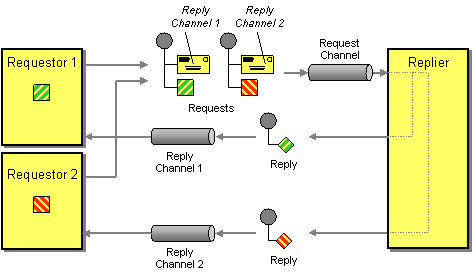
The Return Address EIP facilitates adding a return address to a request message, which indicates where to send the reply message. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/ReturnAddress.html.
Figure 1: Return Address EIP
Example scenario
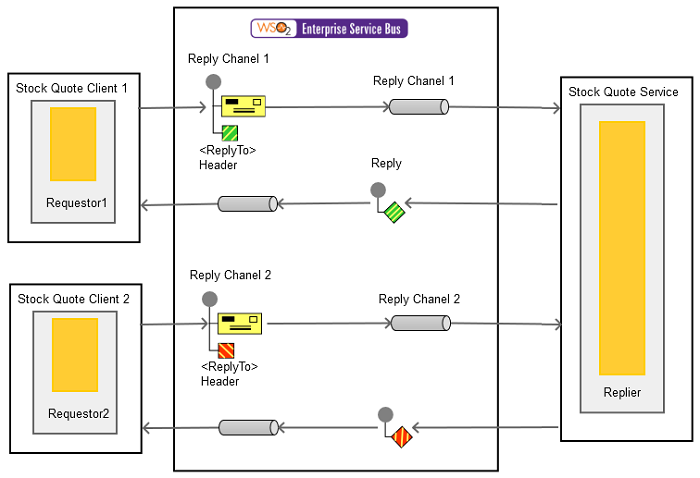
This example is a stock quote service where a client sends a stock quote request to WSO2 ESB with a return address embedded in the message header, which will indicate to the replier where the response message should be sent.
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using WSO2 ESB.
Figure 2: Example Scenario of the Return Address EIP
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Return Address EIP by comparing their core components.
| Return Address EIP (Figure 1) | Return Address Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Requestor 1 | Stock Quote Client Instance |
| Request Channel 1 | Send Mediator |
| Requestor 2 | Stock Quote Client Instance |
| Request Channel 2 | Send Mediator |
| Replier | Stock Quote Service Instance |
Environment setup
- Download and install WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, refer to Installation Guide in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Start the sample Axis2 server. For instructions, refer to the section Setting Up the ESB Samples - Starting the Axis2 server in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ESB configuration
Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (https://localhost:9443/carbon). In the management console, navigate to the Main menu and click Source View in the Service Bus section. Next, copy and paste the following configuration, which helps you explore the example scenario, to the source view.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<sequence name="main">
<in>
<log level="full"/>
<send/>
</in>
<out>
<log level="full"/>
<send/>
</out>
</sequence>
</definitions>
Simulating the sample scenario
- Send a request using the Stock Quote client to WSO2 ESB in the following manner. For information about the Stock Quote client, refer to the Sample Clients section in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ant stockquote -Daddurl=http://localhost:9000/soap/SimpleStockQuoteService -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:8280/ -Dmode=dualquote -Dsymbol=foo
If you use TCPmon to analyze the message passing, you will notice that the client sends the following message. Note that in line 4, the WS-Addressing
ReplyToheader is set to a service called anonService2. Since the reply is made to this service on a separate channel, the client will receive no response.<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <soapenv:Header xmlns:wsa="http://www.w3.org/2005/08/addressing"> <wsa:To>http://localhost:9000/service/SimpleStockQuoteService</wsa:To> <wsa:ReplyTo> <wsa:Address>http://10.150.3.53:8200/axis2/services/anonService2/</wsa:Address> </wsa:ReplyTo> <wsa:MessageID>urn:uuid:9aa8e783-2eb7-4649-9d36-a7fb3ad17abd</wsa:MessageID> <wsa:Action>urn:getQuote</wsa:Action> </soapenv:Header> <soapenv:Body> <m0:getQuote xmlns:m0="http://services.samples"> <m0:request> <m0:symbol>foo</m0:symbol> </m0:request> </m0:getQuote> </soapenv:Body> </soapenv:Envelope>
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below are mapped with the ESB configuration shown above.
- send [line 10 in ESB config] - The
sendmediator forwards messages to the address implied in theReplyToheader field by default, unless it is made explicit that the reply should go to a specific address by using an endpoint mediator.