The content in this documentation is for older versions of WSO2 products. For updated information on Enterprise Integration Patterns, go to the latest Micro Integrator documentation.
Event-Driven Consumer
This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Event-Driven Consumer EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Event-Driven Consumer
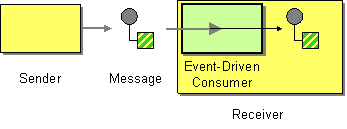
The Event-Driven Consumer EIP allows an application to automatically consume messages as they become available. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/EventDrivenConsumer.html.
Figure 1: Event-Driven Consumer EIP
Example scenario
This EIP is also referred to as an asynchronous receiver. This example scenario demonstrates how an event will be triggered based on the availability of the receiver and a message will be consumed by the receiver.
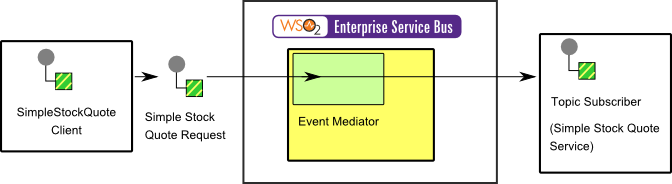
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using WSO2 ESB.
Figure 2: Example scenario of the Event-Driven Consumer EIP
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Event-Driven Consumer EIP by comparing their core components.
| Event-Driven Consumer EIP (Figure 1) | Event-Driven Consumer Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Sender | Simple Stock Quote Client |
| Message | Simple Stock Quote Request |
| Event Driven Consumer | Event Mediator |
| Receiver | Simple Stock Quote Service |
Environment setup
- Download and install WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, see the Installation Guide in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Start two sample Axis2 server. For instructions, see Setting Up the ESB Samples - Starting the Axis2 server in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Follow the steps below to create an event.
- Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (
https://localhost:9443/carbon). - Select the Topics menu from the Main menu and then select the Add sub menu.
- Enter
EventConsumerTopicas the name for the topic, and then click Add Topic. - Click the newly created topic EventConsumerTopic in the topic browser tree and click Subscribe to create a static subscription.
- Enter the value
http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteServicein the Event Sink URL field and click Subscribe.
- Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (
ESB configuration
On the ESB's Management Console, navigate to the Main menu and click Source View in the Service Bus section . Next, copy and paste the following configuration, which helps you explore the example scenario, to the source view.
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<sequence name="fault">
<log level="full">
<property name="MESSAGE" value="Executing default "fault" sequence"/>
<property name="ERROR_CODE" expression="get-property('ERROR_CODE')"/>
<property name="ERROR_MESSAGE" expression="get-property('ERROR_MESSAGE')"/>
</log>
<drop/>
</sequence>
<sequence name="main">
<log/>
<event topic="EventConsumerTopic"/>
</sequence>
</definitions>
Simulating the sample scenario
Send a request using the Stock Quote client to the ESB as follows. For information about the Stock Quote client, see the Sample Clients section in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ant stockquote -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:8280 -Dsymbol=foo
After sending the request, note that a message accepting the request is displayed on the Stock Quote service's console. This is triggered as an event when the message is published to
EventConsumerTopicthat you created earlier. All subscribers will receive the topic.
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below are mapped with the ESB configuration shown above.
- event [line 13 in ESB config] - Allows you to define a set of subscribers to receive messages when the topic subscribes to receives a message. Also, see Eventing.