The content in this documentation is for older versions of WSO2 products. For updated information on Enterprise Integration Patterns, go to the latest Micro Integrator documentation.
Content Enricher
This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Content Enricher EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Content Enricher
The Content Enricher EIP facilitates communication with another system if the message originator does not have all the required data items available. It accesses an external data source to augment a message with missing information. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/DataEnricher.html.
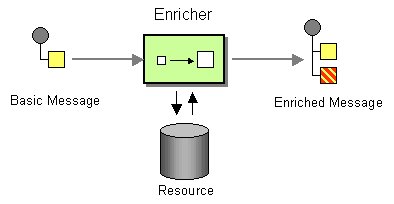
Figure 1: Content Enricher EIP
Example scenario
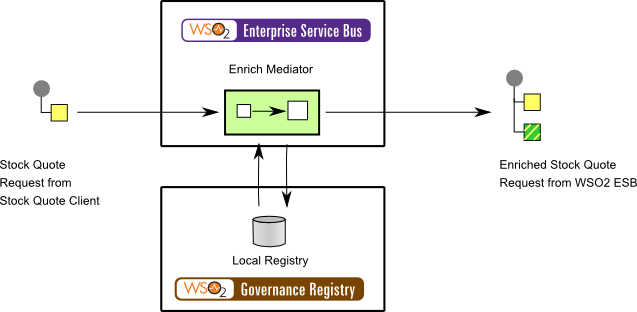
This example scenario depicts a stock quote service. The client sends a stock quote request to the ESB with only an identity number. But in order to provide a stock quote, the sample Axis2 server at the back-end needs to map the identity number with a corresponding name, which is in an external source. The values are stored in the registry as a local entry. When the request arrives, the identity will be analyzed using the Switch mediator. Sequentially, the identity number will be replaced with the local entry using the Enrich mediator.
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using the WSO2 ESB.
Figure 2: Example Scenario of the Content Enricher EIP
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Content Enricher EIP by comparing their core components.
| Content Enricher EIP (Figure 1) | Content Enricher Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Basic Message | Stock Quote Request from Stock Quote Client |
| Enricher | Enrich Mediator |
| Resource | Local Registry |
| Enriched Message | Enriched Stock Quote Request from WSO2 ESB |
Environment setup
- Download and install WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, refer to Installation Guide in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Start the sample Axis2 server. For instructions, refer to the section Setting Up the ESB Samples - Starting the Axis2 server in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ESB configuration
Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (https://localhost:9443/carbon). In the management console, navigate to the Main menu and click Source View in the Service Bus section. Next, copy and paste the following configuration, which helps you explore the example scenario, to the source view.
<!-- Content Enricher -->
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<proxy name="ContentEnrichProxy">
<target>
<inSequence>
<!-- Would Enrich the Value Based On the Number -->
<switch source="//m1:symbol" xmlns:m0="http://services.samples" xmlns:m1="http://services.samples/xsd">
<case regex="1">
<log level="full" />
<enrich>
<source type="inline" key="Location1"/>
<target xmlns:m1="http://services.samples/xsd" xpath="//m1:symbol/text()"/>
</enrich>
</case>
<case regex="2">
<enrich>
<source type="inline" key="Location2"/>
<target xmlns:m1="http://services.samples/xsd" xpath="//m1:symbol/text()"/>
</enrich>
</case>
</switch>
<!--Will Send the Enriched Message -->
<send>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService" />
</endpoint>
</send>
<!-- <drop /> -->
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send />
</outSequence>
</target>
<publishWSDL uri="file:repository/samples/resources/proxy/sample_proxy_1.wsdl"/>
</proxy>
<localEntry key="Location1">IBM</localEntry>
<localEntry key="Location2">WSO2</localEntry>
</definitions>
Simulating the sample scenario
Send the following request to the ESB using a SOAP client like SoapUI.
<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:ser="http://services.samples" xmlns:xsd="http://services.samples/xsd">
<soapenv:Header/>
<soapenv:Body>
<ser:getQuote>
<!--Optional:-->
<ser:request>
<!--Optional:-->
<xsd:symbol>2</xsd:symbol>
</ser:request>
</ser:getQuote>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope>
Note that the Axis2 server log displays that the request is processed.
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below are mapped with the ESB configuration shown above.
- enrich [line 10 in ESB config] - Mediator used for message enrichment.
- source [line 11 in ESB config] - The location in which you can find the source configuration. In this example, it is a simple inline text string located in the local registry entry with key Location1.
- target [line 12 in ESB config] - The location where the source configuration should be applied. This is specified using an XPath expression.
- localEntry [lines 36 and 37 in ESB config] - Entries from the local registry.