The content in this documentation is for older versions of WSO2 products. For updated information on Enterprise Integration Patterns, go to the latest Micro Integrator documentation.
Detour
This section explains, through an example scenario, how the Detour EIP can be implemented using WSO2 ESB. The following topics are covered:
Introduction to Detour
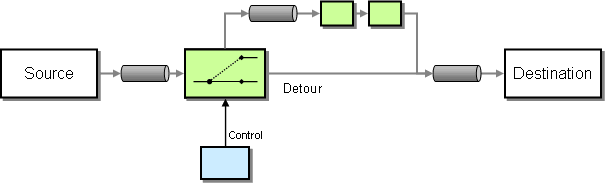
The Detour EIP routes a message through intermediate steps to perform validation, testing, or debugging functions. Detour has two states. In one state, the router routes incoming messages through additional steps, while in the other, it routes messages directly to the destination channel. For more information, refer to http://www.eaipatterns.com/Detour.html.
Figure 1: Detour EIP
Example scenario
This example scenario demonstrates how to use the Filter and Validate mediators of WSO2 ESB to implement the Detour pattern. First, the message is filtered using the source and regex parameters. Next the filtered message is validated. Messages are then forwarded to the appropriate destination.
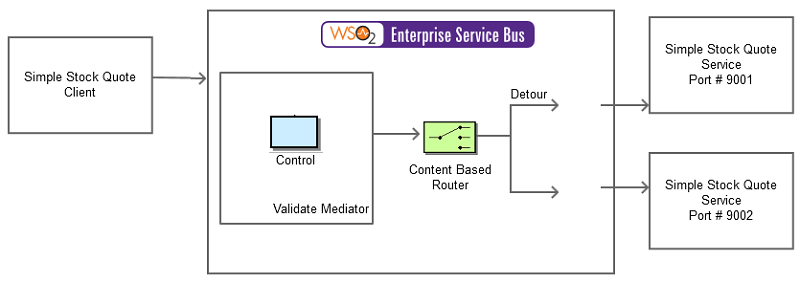
The diagram below depicts how to simulate the example scenario using the WSO2 ESB.
Figure 2: Example Scenario of the Detour EIP
Before digging into implementation details, let's take a look at the relationship between the example scenario and the Detour EIP by comparing their core components.
| Detour EIP (Figure 1) | Detour Example Scenario (Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Source | Simple Stock Quote Client |
| Control | XML Schema Validation using Validate Mediator |
| Detour | Content Based Routing |
| Destination | Simple Stock Quote Service |
Environment setup
- Download and install WSO2 ESB from http://wso2.com/products/enterprise-service-bus. For a list of prerequisites and step-by-step installation instructions, refer to Getting Started in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
- Start a sample Axis2 server instance on port 9000. For instructions, see ESB Samples Setup - Starting Sample Back-End Services in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ESB configuration
Start the ESB server and log into its management console UI (https://localhost:9443/carbon). In the management console, navigate to the Main menu and click Source View in the Service Bus section. Next, copy and paste the following configuration, which helps you explore the example scenario, to the source view.
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<localEntry key="validate_schema">
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns="http://services.samples"
elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified"
targetNamespace="http://services.samples">
<xs:element name="getQuote">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="request">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="stocksymbol" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
</localEntry>
<sequence name="fault">
<log level="full">
<property name="MESSAGE" value="Executing default "fault" sequence"/>
<property name="ERROR_CODE" expression="get-property('ERROR_CODE')"/>
<property name="ERROR_MESSAGE" expression="get-property('ERROR_MESSAGE')"/>
</log>
<drop/>
</sequence>
<sequence name="main">
<in>
<filter source="get-property('To')" regex=".*StockQuote.*">
<validate>
<schema key="validate_schema"/>
<on-fail>
<makefault>
<code xmlns:tns="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope" value="tns:Receiver"/>
<reason value="Invalid custom quote request"/>
</makefault>
</on-fail>
</validate>
</filter>
<send/>
</in>
<send/>
</sequence>
</definitions>
Simulating the sample scenario
Send a request using the Stock Quote client to WSO2 ESB in the following manner. For information about the Stock Quote client, refer to the section Sample Clients in the WSO2 ESB documentation.
ant stockquote -Daddurl=http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:8280
Based on the To endpoint reference of http://localhost:9000/services/SimpleStockQuoteService, the ESB performs a comparison to the path StockQuote, and if the request matches the XPath expression of the filter mediator, the filter mediator's child mediators will be executed. Next, the child mediators start validating the request. Because we are sending the stockquote request using ant stockquote ... commands, we will get a fault as 'Invalid custom quote request'. This indicates that the schema validation has failed, which happens because the schema used in the example expects a stocksymbol element instead of a symbol to specify the stock symbol.
How the implementation works
Let's investigate the elements of the ESB configuration in detail. The line numbers below refer to the ESB configuration shown above.
- localEntry [line 2 in ESB config] - Specifies a local entry containing the XML schema to use for validation.
- sequence [line 31 in ESB config] - The main sequence for the ESB, which is the default sequence.
- filter [line 33 in ESB config] - The filter mediator that is used to provide content based routing. In this case, the SOAP Header field
Tois matched against a regular expression that checks to see whether theTofield containsStockQuote. - validate [line 34 in ESB config] - Performs validation on the SOAP body using the XML Schema defined in the
localEntry(line 2 in ESB config). - on-fail [line 36 in ESB config] - If the validation fails, the on-fail element provides a detour, which can be used to channel the message through a different route and ultimately passed on to the intended service. In the example scenario, a fault is produced and the fault is sent back to the requesting client.
- send [line 44 in ESB config] - the send mediator is used to send the message to the intended receiver - however if the
makeFaultinside the on-fail element (line 37 in ESB config) is executed before this mediator is reached, then the fault is returned to the requesting client.